Stena
Stent Esophageal System
The Esophageal Stent aims to provide lumen patency through a combination of flexibility and control to support your goal of optimized patient care. It is used to expand the esophagus, cardia and anastomosis, bloat stricture and esophageal obstruction. The Esophageal Stent is indicated for use in the treatment of esophageal strictures produced by malignant neoplasms, cardiac stenosis, anastomotic stomatal stenosis and fistula blockade treatment of esophageal fistula.
| Components | Titanium, Nickel | |
| Structure | Titanium, Nickel | |
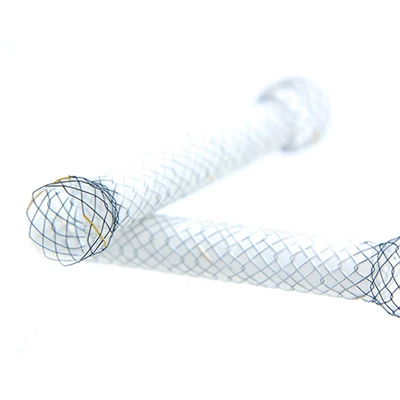
| Form | Cylindrical with one or two ends, cylindrical rim, bowl rim, spherical or cork | |
| Scale | Diameter: 16-22mm; Length: between 40-120 mm. | |
| Purpose of Usage | It is used for the expansion treatment of esophageal stenosis, cardiac stenosis and anastomotic stenosis, and for the fistula-blocking treatment of esophageal fistula. |


Detailed specifications
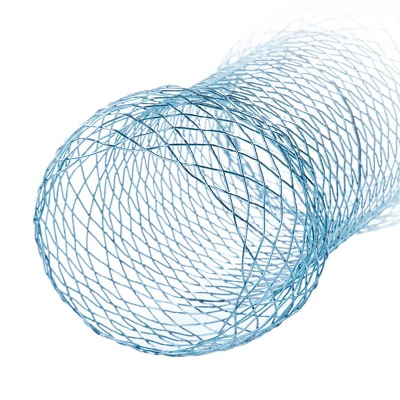
Nitinol self-expandable stents are composed of a shape memory titanium nickel alloy that is biocompatible and erosion resistant and has stable shape memory and superelasticity properties. Under conditions in the human body and a temperature of more than 33 degrees, the stent will gradually expand its original shape after being released from the introducer. The stent will then generate a slight radial pulling force, progressively widening the stenosis and rebuilding an unobstructed canal.
Inside the human body and below body temperature, stents will reach their super-elasticity and cause less potential discomfort for patients.
The design of these specially constructed stents
In addition, it reduces the patient's discomfort.
Both ends of the stent are bendable and smooth, with no sharp edges and no spikes to reduce the risk of injuring the esophageal wall.
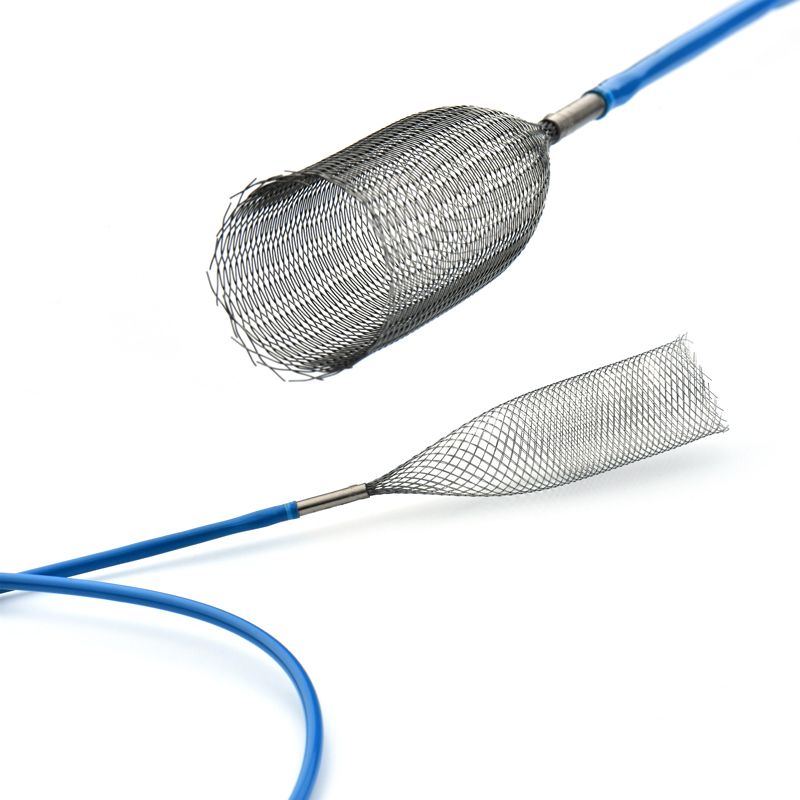
The delivery system consists of an introducer and a preloaded esophageal stent and is used to guide and release the stent at the designated location.
It is designed for proximal stent placement. When working with these sets, the stent can be retracted into the outer tube for repositioning, provided that the stent is completely released from the applicator (at least 30 mm may still be within the applicator).
Postoperative anastomotic stoma dilated multiple times with no effect.
Rebound carcinoma
Cardia achalasia,
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Mediastenesophageal fistula.
The Esophageal Stent System consists of two components: the implantable metallic stent and the Esophageal Stent delivery system. The stent consists of nitinol wire braided into a tubular braid. This design configuration results in a flexible, conformable stent that is self-expanding. The docking system is partially composed of coaxial tubes. the outer tube ensures that the stent does not open unintentionally until it is withdrawn during insertion. Radiopaque marker bands on the inner and outer tubes aid imaging during deployment. Stents have radiopaque markers to ensure radiopacity.
The stent is a hollow tube made of a flexible alloy mesh. Stents can be wrapped tightly around the size of a pen to allow them to be inserted through a blockage or tumor in the esophagus or intestine. Once in place, the stents are allowed to expand and therefore keep the passage through the tumor open.
Immigration Resistance
Progressive Step Extended Tips can assist in securing the stent in the esophageal lumen.
Narrowness Resolution
The multi-wire mesh construction is designed to allow the stent to adapt to forces from the esophageal anatomy, such as strictures and peristalsis. The design allows for gradual stent expansion, which is usually completed after 24-72 hours.
Tissue Growth Prevention
Permalume™ Silicone Coating extends the entire length of the stent in the fully closed version and is designed to prevent tumor growth as well as stent-concurrent esophageal fistulas.
Adjustability
The Coated Polyester Removal Suture facilitates removal during the initial stent placement procedure.
Fluoroscopic Visualization
The nitinol construction ensures accurate stent placement, providing clear visualization during fluoroscopy.
|
Name:
|
Coated Esophageal Stents made of Shape memory Titanium-Nickel Alloy
|
|
Components:
|
Titanium, Nickel
|
|
Structure:
|
Braided Stents
|
|
Form:
|
Cylindrical with one or two ends, cylindrical rim, bowl rim, spherical or cork
|
|
Scale:
|
Diameter: 16-22mm; Length: between 40-120 mm.
|
|
Purpose of usage:
|
It is used for the expansion treatment of esophageal stenosis, cardiac stenosis and anastomotic stenosis, and for the fistula-blocking treatment of esophageal fistula.
|